Implementing TCFD Guidance
Recognizing the Impacts of Climate Change Risks
Climate change is primarily caused by the excessive emission of greenhouse gases. Climate change poses severe risks to the impacting all sectors. To drive business growth while addressing this challenge, our company utilizes the Science-Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) to analyze financial impacts. We have developed strategies to effectively manage climate-related risks, aiming to maximize effectiveness. This includes setting short, medium, and long-term goals to reduce carbon emissions, aligned with scenario analysis to control global temperature rise within 1.5 degrees. Moreover, we enhance financial disclosure practices related to climate change following TCFD standards and establish a task force to review and develop our business plans, both direct and indirect, considering the potential systemic impacts of climate change in line with our company's guidelines and policies.
1. Climate Governance Structure
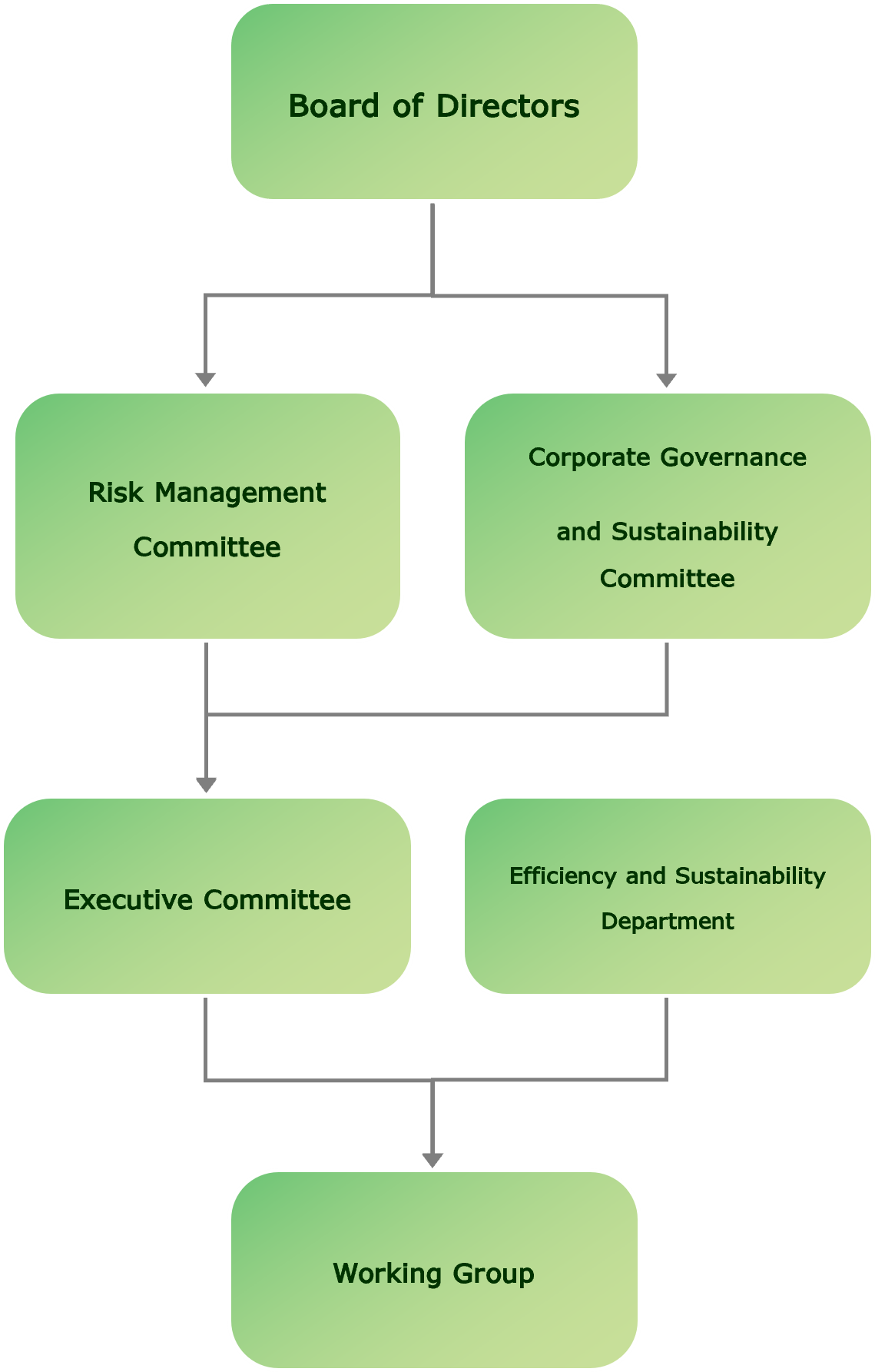
Board of Directors
Oversee, monitor, and follow up on the implementation of climate-related risk to ensure compliance with the company's policies at least once per year.
Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee
Monitor climate-related issues that impact the company, such as internal energy consumption and greenhouse gas reduction targets. Report directly to the company's board of directors at least twice a year.
Risk Management Committee
Establish risk management guidelines, policies, and frameworks. Provide risk recommendations to each department at least twice a year.
Executive Committee
Develop a sustainable development policy and create an appropriate plan for the working group to comply with the policies and practices set by the board of directors.
Efficiency and Sustainability Department
Be responsible for preparing and presenting reports to management to update on the progress of operational activities at least twice a year.
Working Group
Collect and analyze data that is relevant and consistent with the company's sustainability policy.
2. Risks and Opportunity Management
The company integrates the identification and assessment of climate-related risks into its overall risk management process, considering both physical and transition risks. Establish appropriate procedures for comprehensive risk assessment within the organization, including identification, assessment and alleviation of potential impacts on customers, employees and the business. This is conducted regularly at least twice a year, to stay abreast of evolving trends and potential impacts. The company categorizes climate-related risks such as strategic, legal, financial, and technology risks by timeframe(short, medium and long term). Monitors the result of these risks using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) linked to the identified risks, enabling ongoing evaluation and assessment of risk management plans.
Processes of Climate-related Risk Consideration
- Risk Identification Every department participates in identifying climate-related risks that may affect the company's operations annually. The Efficiency and Sustainability Department manages the process, collects the risks, and monitors the results.
- Risk Assessment Every department participates in assessing risks and opportunities. The risks and opportunities identified by each department will be approved by the Executive Committee for the development of management plans to address and mitigate potential impacts.
- Risk Mitigation The risks are divided into two categories: Physical Risks and Transition Risks. The responsibilities and management steps are defined as follows: 1. Physical Risks: Each department must report the results of risk and opportunity management to the Executive Committee, to summarize and compile key issues for presentation to the Risk Management Committee and the Corporate and Sustainability Committee at least twice a year. 2. Transition Risks: The Executive Committee presents policies and operational frameworks to the Risk Management Committee for feedback and consideration in developing management and mitigation plans. High-risk issues must be monitored and the management plans updated every two years.
In 2024, the company continues to prioritize driving business growth while adapting to various scenarios, both direct and indirect, that may arise from climate change. This includes implementing appropriate risk management practices and developing risk management plans aligned with the issue of global temperature rise, aiming to create stability and resilience in business operations. The analysis of risks and opportunities is summarized as follows:
| Category | Risks | Impacts | Short term | Medium term | Long term | Risk Mitigation | KRI | ||||
| Impacts | Likelihood | Impacts | Likelihood | Impacts | Likelihood | ||||||
|
Physical Risks |
Acute Natural Disasters |
|
|
4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
|
|
| Chronic Natural Disasters |
|
4
2
|
2
1
|
5
5
|
3
2
|
5
5
|
3
3
|
Value of damages not exceeding 1 million baht | |||
| Transition Risks | Legal and Policy-related Risk |
|
|
3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
|
Increased expenses due to environmental regulatory compliance not exceeding 1 million baht |
| Technology-related Risk |
|
|
3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|
Expenditure on alternative energy use not exceeding 1 million baht | |
| The reduced ability to repay debts due to climate change |
|
|
4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
|
NPL not exceeding 5% | |
| The risk of not achieving the Net Zero Company target |
|
|
3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
|
Greenhouse gas emissions have decreased by 10% | |
| Category | Opportunities | Definitions of Opportunities | Benefits | Short term | Medium term | Long term | Respond to Opportunities(Present – 5 Years Ahead) | ||||
| Impacts | Likelihood | Impacts | Likelihood | Impacts | Likelihood | ||||||
| Opportunity |
Products / Services | Low-carbon Products | Issuing credit for low-carbon products and services to help mitigate the impact of climate change |
|
4 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
|
| Energy Source | Renewable energy | The increase in renewable energy sources which have minimal environmental impact such as solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectricity |
|
3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
|
|
3. Climate-related Scenario Analysis
Operating a business in a climate of uncertainty due to changing weather conditions can have a direct impact on the company’s operations. Analyzing climate-related impacts through scenario analysis is essential to enable the business to plan and adapt effectively in a timely manner, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
| Financial Impact (Million Baht) |
|||||||
| Category | Risks | Scenario | Assumption | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
|
Physical Risks |
Acute | Flood | Achieving Net Zero Carbon Emissions by 2050 (SSP1-2.6) |
% Change in rain average largest
5-day cumulative precipitation =
% NPL impact due to disaster |
3,587 | 3,628 | 3,669 |
| Doubling Carbon Dioxide Emissions by 2050 (SSP5-8.5) |
% Change in rain average largest 5-day cumulative precipitation = % NPL impact due to disaster |
3,658 | 3,726 | 3,793 | |||
|
Transition Risks |
Legal and Policy | Carbon Tax | Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS) | Thai’s implementation of taxing carbon emission will be done in the next 17 year (by 2040) for all sectors in line with Singapore’s carbon tax structure | - | 198.7 | 445.1 |
| Net-Zero Emission Scenario (NZE) | Thai’s implementation of taxing carbon emission will be done in the next 7 year (by 2030) for all sectors in line with Singapore’s carbon tax structure | 78.9 | 238.5 | 498.5 | |||